Synchrotron photon sources offer an extremely wide energy spectrum, ultra-small beam dimensions and extreme temporal resolution, making it possible to investigate a huge range of dynamic processes in materials and biological systems.
At IPS we develop and apply synchrotron-based in situ & operando X-ray imaging, X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray scattering techniques within the framework of the Helmholtz Research Program "From Matter to Materials and Life" (MML). Our research comprises pioneering, proof-of-principle experiments as well as systematic studies, which advance our understanding of the relationships between structure, function and behaviour in materials research and the life sciences. For this purpose the IPS operates the three state-of-the-art SPECTROSCOPY, SCATTERING and IMAGING Clusters, incorporating beamline and laboratory instrumentation at the KIT Light Source together with facilities at the synchrotron sources at PETRA III, the ESRF and the ALS.
Our research activities are closely linked to teaching and research within the KIT Faculties of Physics and Chemistry & Biosciences, and we work in close cooperation with other KIT institutes and with leading national and international research institutions and universities.
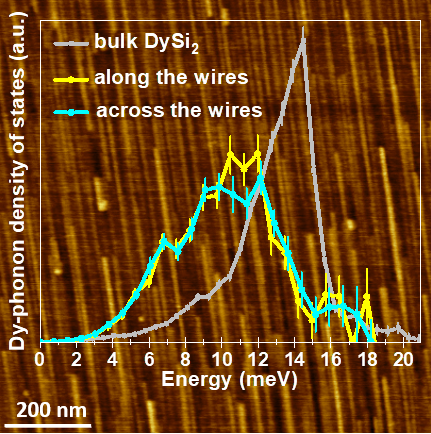
The evolution of the atomic vibrations, described by the phonon density of states, from the bulk material to self-organized nanoislands and nanowires of the technology relevant rare earth silicide DySi2 is investigated. The results do not only clarify structural characteristics and unveil anomalies in important properties of this material, they also suggest strategies for their tailoring.
more
We welcome Dr. Julian Katzke, KIT International Excellence Fellow, for a three-month stay at IPS. He brings expertise in X-ray µCT, morphometrics, and machine learning, and will help develop scalable workflows to advance morphological imaging and digital biodiversity research.
more
Jenny Hein & Thomas van de Kamp received three awards for their contribution “A Bark Beetle’s Stellar Gut” at the Best Scientific Image Contest 2025 of Helmholtz Imaging. Their work features a 3D synchrotron scan revealing the star-shaped foregut of a bark beetle - a stunning look into insect inner morphology.
more